Aug 23, · DNA occurs in five forms: A-DNA, B-DNA, C-DNA, D-DNA, and Z-DNA. The B form occurs in most organisms and is a right-handed helix with a major and minor groove. The main types of RNA are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA A lagging strand is the name for one of the two DNA strands in a double helix that is undergoing replication. This lesson will explain which strand is lagging and how it is replicated DNA replication: ¥Complementary base pairing produces semiconservative replication ÐDouble helix unwinds ÐEach strand acts as template ÐComplementary base pairing ensures that T signals addition of A on new strand, and G signals addition of C Homework
DNA vs RNA - Similarities and Differences
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is the molecule that codes genetic information. However, DNA can't directly order a cell to make proteins.
It has to be transcribed into RNA or ribonucleic dna replication homework. RNA, in turn, is translated by cellular machinery to make amino acids, which it joins together to form polypeptides and proteins. Transcription is the first stage of the expression of genes into proteins.
In transcription, an mRNA messenger RNA intermediate is transcribed from one of the strands of the DNA molecule. The RNA is called messenger RNA because it carries the "message," or genetic information, from the DNA to the ribosomeswhere the information is used to make proteins.
RNA and DNA use complementary coding where base pairs match up, similar to how the strands of DNA bind to form a double helix. One difference between DNA and RNA is that RNA uses uracil in place of the thymine used in DNA. RNA polymerase mediates the manufacture of an RNA strand that complements the DNA strand, dna replication homework. There are some proofreading mechanisms for transcription, but not as many as for DNA replication. Sometimes coding errors occur.
There are significant differences in the process of transcription in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes. Transcription can be broken into five stages: pre-initiation, dna replication homework, initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination:. The first step of transcription is called pre-initiation. RNA polymerase and cofactors general transcription factors bind to DNA and unwind it, creating an initiation bubble.
It's similar in appearance to what you get when you unwind strands of multi-ply yarn, dna replication homework. This space grants RNA polymerase access to a single strand dna replication homework the DNA molecule. Approximately 14 base pairs are exposed at a time. The initiation of transcription in bacteria begins with the binding dna replication homework RNA polymerase to the promoter in DNA. Transcription initiation is more complex in eukaryotes, where a group of proteins called transcription factors mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
The next step of transcription is called promoter clearance or promoter dna replication homework. RNA polymerase must clear the promoter once the first bond has been synthesized. The promoter is a DNA sequence that signals which DNA strand is transcribed and the direction transcription proceeds.
Approximately 23 nucleotides must be synthesized before RNA polymerase loses its tendency to slip away and prematurely release the RNA transcript. One strand of DNA serves as the template for RNA synthesis, but multiple rounds of transcription may occur so that many copies of a gene can be produced. Termination is the final step of transcription. Termination results in the release of the newly synthesized mRNA from the elongation complex. In eukaryotes, the termination of transcription involves cleavage of the transcript, followed by a process called polyadenylation.
In polyadenylation, a series of adenine residues or poly A tail is added to the new 3' end of the messenger RNA dna replication homework. Share Flipboard Email, dna replication homework. Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph. Chemistry Expert. Helmenstine holds a Ph. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, dna replication homework, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
our editorial process. Facebook Facebook Twitter Twitter. Updated March 02, RNA, in turn, is translated by cellular machinery to make amino acids, which it joins together to form polypeptides and proteins Overview of Transcription Transcription is the first stage of the expression of genes into proteins.
Differences in Transcription There are significant differences in the process of transcription in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes, dna replication homework. In prokaryotes bacteriatranscription occurs in the cytoplasm. Translation of the mRNA into proteins also occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm for translation. DNA in prokaryotes is much more accessible to RNA polymerase than DNA in eukaryotes.
Eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones to form structures called nucleosomes. Eukaryotic DNA is packed to form chromatin. While RNA polymerase interacts directly with prokaryotic DNA, other proteins mediate the interaction between RNA polymerase and Dna replication homework in eukaryotes.
mRNA produced as a result of transcription is not modified in prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA by RNA splicing, 5' end capping, and addition of a polyA tail.
Key Takeaways: Steps of Transcription The two main steps in gene dna replication homework are transcription and translation. Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination. Cite this Article Format.
Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph. Steps of Transcription From DNA to RNA. copy citation. Watch Now: Scientists Want To Store All Information on DNA. Ribosomes - The Protein Builders of a Cell, dna replication homework. Learn About Nucleic Acids and Their Function. Synonymous vs. Nonsynonymous Mutations.
What Is Phosphorylation and How Does It Work?
DNA Replication (Updated)
, time: 8:12Mastering Biology Chapter 16 – RHS Homework
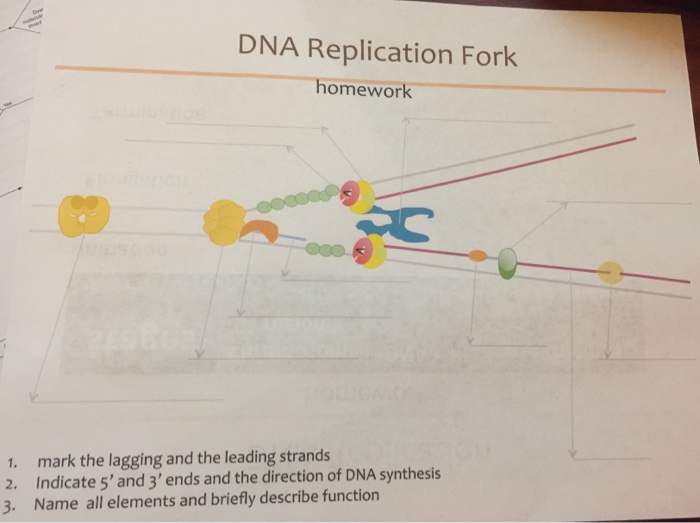
Feb 17, · DNA replication always begins at an origin of replication. In bacteria, there is a single origin of replication on the circular chromosome, as shown in the image here. Beginning at the origin of replication, the two parental strands (dark blue) separate, forming a replication bubble. answers Biology help homework honors mastering biology DNA Interactive is an educational web site resource that celebrates the 50th anniversary of the discovery of the DNA double helix structure. IMPORTANT: Adobe Flash Information. DNA Interactive was built using Flash, which is no longer supported by web browsers. We have installed an open source Flash emulator on the site; it is not perfect, but Aug 23, · DNA occurs in five forms: A-DNA, B-DNA, C-DNA, D-DNA, and Z-DNA. The B form occurs in most organisms and is a right-handed helix with a major and minor groove. The main types of RNA are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA
No comments:
Post a Comment